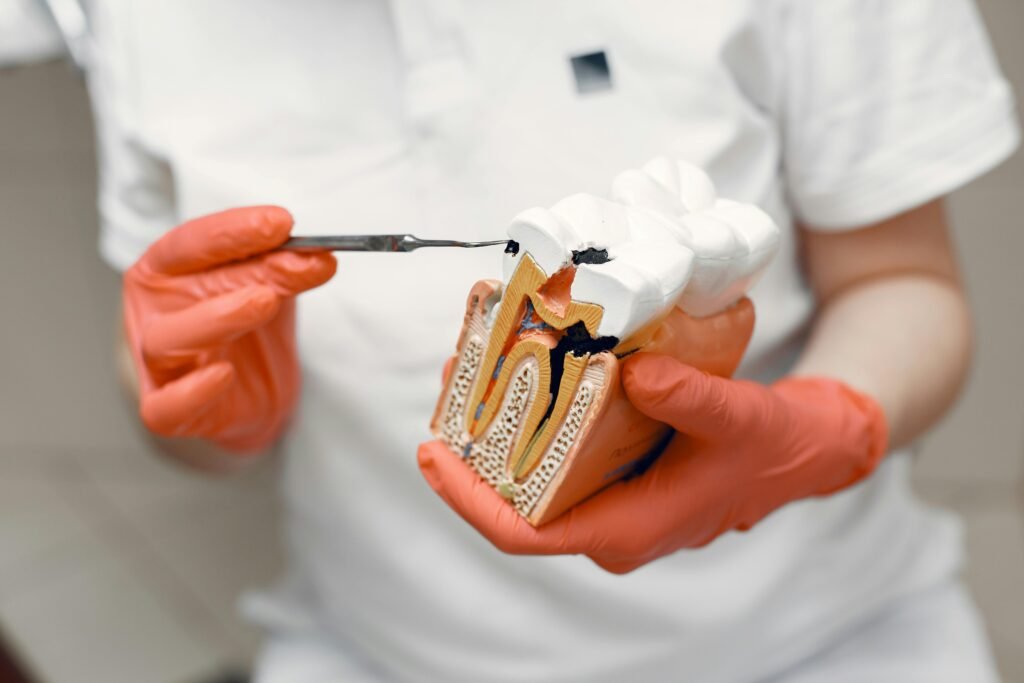
Vital pulp therapy (VPT) is a dental procedure that is used to treat a tooth that has experienced trauma or decay that has affected the pulp, the soft tissue inside the tooth. The aim of VPT is to maintain the vitality of the pulp, meaning to keep the pulp healthy and alive.
Vital pulp therapy is typically used in situations where the pulp is not extensively damaged or infected, and the tooth can be saved without the need for extraction or root canal treatment. The procedure involves removing any damaged or decayed tissue from the pulp, disinfecting the area, and then filling the pulp chamber with a material that promotes healing and encourages new tissue growth.
There are three main types of vital pulp therapy:
– Indirect pulp capping: This procedure is used when decay or trauma has come close to but has not yet reached the pulp. The dentist will remove the decay and place a temporary filling over the area to protect the tooth and encourage the pulp to heal.
– Direct pulp capping: This procedure is used when a small exposure of the pulp has occurred. The dentist will remove any damaged tissue, clean the area, and then apply a biocompatible material directly to the pulp to stimulate healing.
– Pulpotomy: involves the removal of the infected pulp in the crown portion of the tooth, and is performed to preserve the remaining healthy pulp in teeth with reversible pulpitis or shallow decay
Vital pulp therapy can be an effective way to treat damaged or decayed teeth, but it is not always appropriate for every situation. The success of the procedure depends on the extent of the damage to the pulp, the patient’s age and overall health, and their dental history.
What are the materials used in vital pulp therapy?
There are several materials used in vital pulp therapy, depending on the specific procedure and the preference of the dentist. Here are some common materials used in vital pulp therapy:
– Calcium hydroxide: This material is often used in indirect pulp capping procedures to stimulate the pulp to produce new dentin, the hard tissue that makes up the bulk of the tooth. Calcium hydroxide has antimicrobial properties and helps to neutralize acids produced by bacteria in the mouth.
– Mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA): MTA is a biocompatible material that is commonly used in direct pulp capping and pulpotomy procedures. It is made from a mixture of fine powders and has excellent sealing properties to prevent bacterial penetration into the pulp.
– Glass ionomer cement: This material is also used in direct pulp capping and pulpotomy procedures. Glass ionomer cement is biocompatible and releases fluoride, which can help to reduce the risk of further decay.
– Adhesive resin: In some cases, an adhesive resin may be used to bond a restoration, such as a filling or crown, to the tooth after vital pulp therapy.
The choice of material depends on the specific needs of the tooth and the patient, as well as the preference of the dentist. The dentist will consider factors such as the extent of the damage to the pulp, the location of the tooth in the mouth, and the overall oral health of the patient when selecting a material for vital pulp therapy.
What is a contraindication for vital pulp therapy?
Vital pulp therapy is generally considered a safe and effective treatment for teeth with damaged or decayed pulp. However, there are some situations where vital pulp therapy may not be appropriate. A contraindication for vital pulp therapy is any factor that would make the procedure ineffective or potentially harmful to the patient.
Some common contraindications for vital pulp therapy include:
– Pulp necrosis: If the pulp is already dead or severely infected, vital pulp therapy is not recommended as it will not be effective in saving the tooth.
– Periapical pathology: If there is an infection or abscess at the tip of the tooth root, vital pulp therapy may not be effective in treating the underlying issue.
– Trauma to the tooth: If the tooth has suffered severe trauma, such as a fracture that extends into the pulp chamber, vital pulp therapy may not be effective in saving the tooth.
– Large pulp exposure: If the exposure of the pulp is too large or the pulp has been extensively damaged, vital pulp therapy may not be effective in saving the tooth.
– Patient’s overall health: Certain medical conditions or medications may affect the success of vital pulp therapy. For example, patients with compromised immune systems may be at a higher risk of infection.
It is important to consult with a dentist or endodontist to determine if vital pulp therapy is appropriate for a particular patient and tooth.
What is the success rate of vital pulp therapy?
The success rate of vital pulp therapy can vary depending on several factors, such as the extent of the damage to the tooth, the type of procedure performed, the materials used, and the overall health of the patient. In general, vital pulp therapy has a high success rate, especially when compared to other types of pulp treatments such as root canal therapy or tooth extraction.
Several studies have reported success rates of between 80% and 95% for vital pulp therapy, depending on the type of procedure and the length of follow-up.
For example, a systematic review of direct pulp capping procedures published in the Journal of Endodontics in 2015 reported a success rate of 87.5% over a median follow-up period of 14 months. Another study published in the same journal in 2018 reported a success rate of 94.6% for pulpotomy procedures over a mean follow-up period of 18 months.
Factors that can affect the success rate of vital pulp therapy include the age of the patient, the size of the pulp exposure, the presence of bacteria in the pulp, and the type of material used to fill the pulp chamber. In some cases, the tooth may require additional treatment, such as root canal therapy, if the pulp therapy is not successful.
It is important to discuss the potential risks and benefits of vital pulp therapy with a dentist or endodontist to determine if it is the best treatment option for a particular patient and tooth.