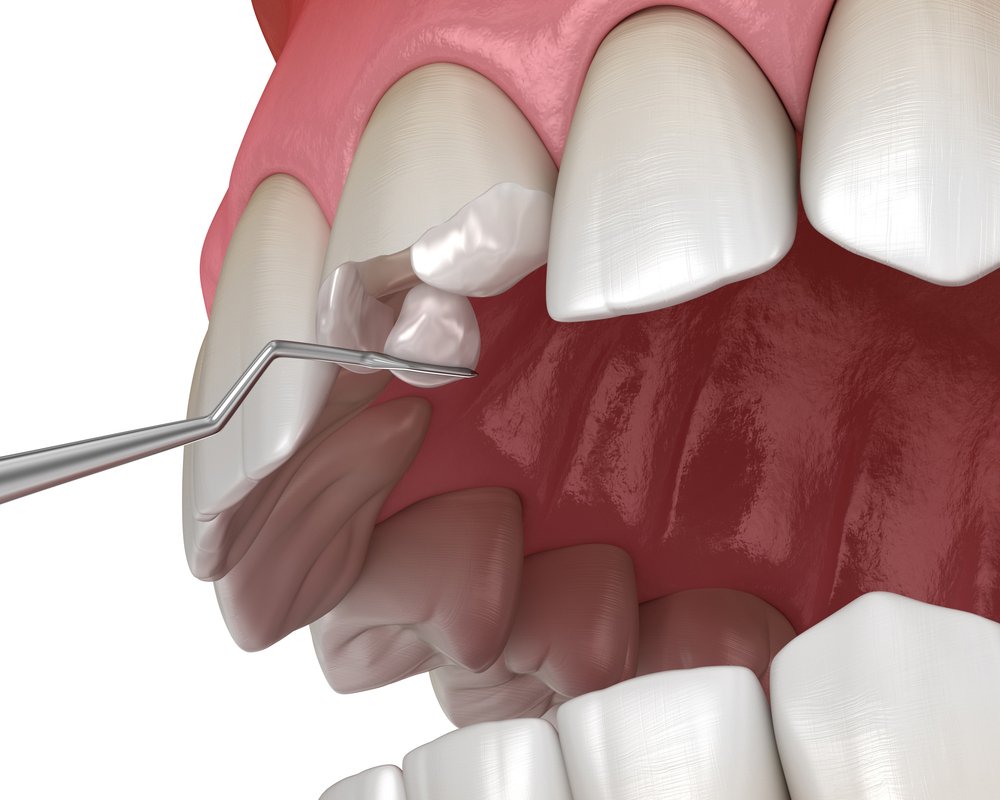
A dental filling restores a tooth’s structure and function after decay, fracture, or wear. At AbuMaizar Dental Center, we provide evidence-based, patient-focused restorations using advanced materials and techniques. Fillings repair teeth, protect the pulp, and prevent infection.
Understanding Tooth Structure
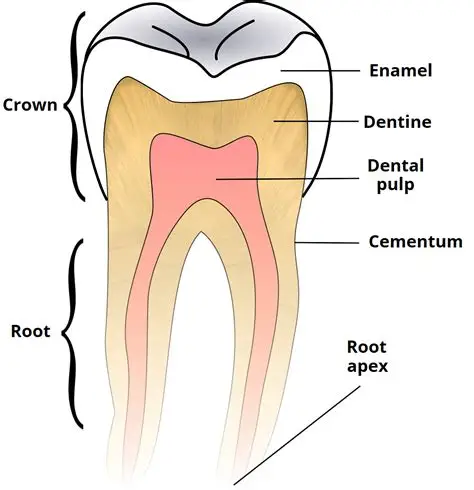
- Enamel: Hard outer layer protecting the tooth from wear and bacteria.
- Dentin: Softer layer beneath enamel containing microscopic tubules connected to the pulp.
- Pulp: Soft tissue containing nerves, blood vessels, and connective tissue.
When decay penetrates enamel into dentin, or trauma exposes dentin or pulp, a filling becomes essential to restore strength and prevent infection.
Why You Might Need a Filling
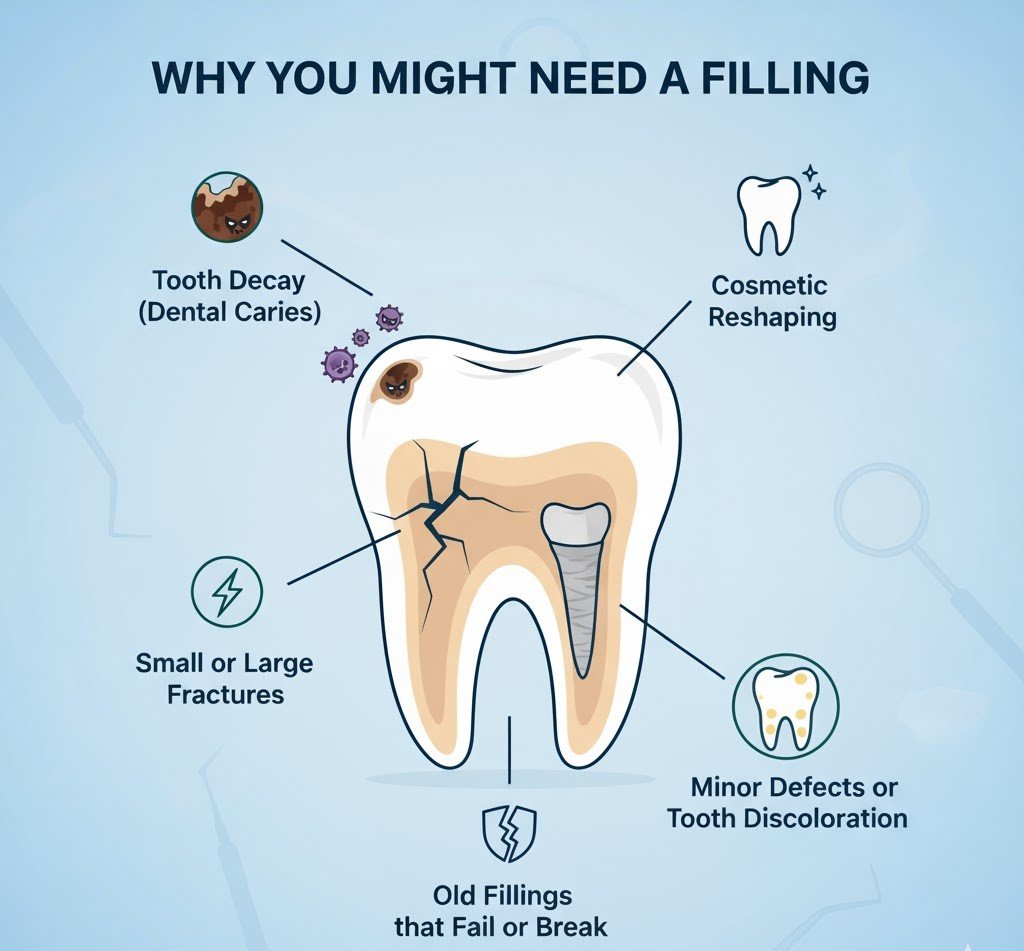
- Tooth decay (dental caries) reaching enamel or dentin
- Small or large fractures
- Old fillings that fail or break
- Cosmetic reshaping
- Minor defects or tooth discoloration
Types of Dental Fillings
| Filling Type | Material | Advantages | Disadvantages | Longevity | Ideal Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composite (Tooth-Colored) | Resin-based (plastic + glass) | Aesthetic, bonds to tooth, preserves structure | Less durable under heavy chewing, may stain over time | 5–15 years | Front and back teeth, visible areas |
| Amalgam (Silver) | Mercury alloy with silver, tin, copper | Durable, cost-effective, strong | Silver color, mercury content concern (safe in adults) | 10–15 years | Posterior teeth under high bite forces |
| Glass Ionomer | Acrylic + glass powder | Releases fluoride, bonds chemically to enamel & dentin | Less durable than composites, prone to wear | 3–7 years | Children, primary teeth, cervical lesions, small cavities |
| Ceramic (Porcelain/Inlay-Onlay) | Lab-fabricated porcelain | Highly aesthetic, stain-resistant, biocompatible | Requires two visits, higher cost | 10–15 years | Cosmetic restorations, inlays/onlays |
| Gold | Gold alloy | Extremely durable, biocompatible, precise fit | Expensive, metallic color | 15–30 years | Inlays/onlays, high-strength posterior restorations |
| Resin Ionomer (Hybrid) | Resin + glass ionomer | Fluoride release, chemical bonding, minimal shrinkage | Less aesthetic than composite | 5–7 years | Pediatric dentistry, small restorations, temporary repair |
Step-by-Step Procedure
- Diagnosis: Visual inspection and X-rays to assess cavity depth and pulp proximity.
- Anesthesia: Local anesthetic numbs the tooth; sedation available for anxious patients.
- Decay Removal: Using dental drill or laser, decayed tissue is removed precisely.
- Tooth Preparation: Shaping, cleaning, and disinfecting the cavity; bonding agent applied for composites.
- Filling Placement: Layered and cured for composites; packed and shaped for amalgam; lab-fabricated ceramic/gold cemented in place.
- Finishing & Polishing: Bite adjusted, surface polished to prevent plaque accumulation.
Benefits of Dental Fillings
- Restores tooth structure and strength
- Prevents pulp infection and further decay
- Improves aesthetics and confidence
- Preserves natural teeth
- Protects long-term oral health and bite function
Aftercare Instructions
- Avoid chewing hard foods for 24–48 hours for new fillings
- Brush and floss carefully around filled teeth
- Use fluoride toothpaste to enhance longevity
- Sensitivity may last 1–2 weeks
- Regular checkups recommended
Potential Complications
- Mild sensitivity or discomfort
- Filling fracture or wear
- Marginal leakage (rare)
- Allergic reactions (extremely rare)
Frequently Asked Questions
Are fillings painful? Modern anesthesia makes fillings virtually painless. Mild sensitivity may occur for a few days.
How long do fillings last? Most fillings last 5–15 years; gold/ceramic can last 20+ years.
Can fillings fail? Yes, due to wear, secondary decay, fracture, or bite issues.
Which filling is best? Composite for visible teeth, amalgam for molars, glass ionomer for children, ceramic/gold for long-lasting posterior restorations.