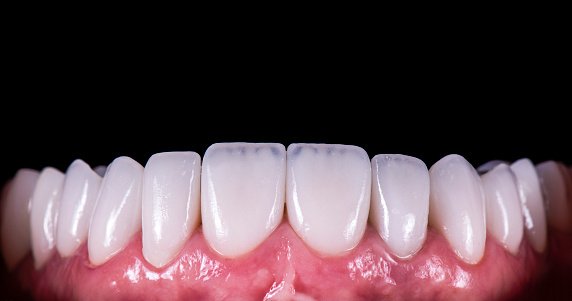
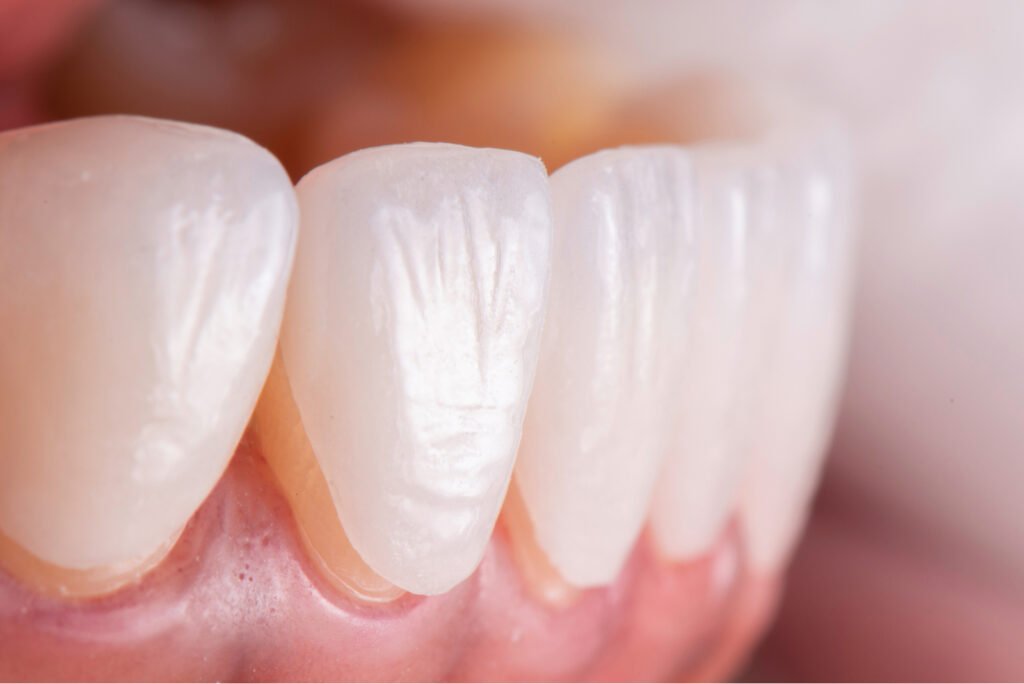
What Are Dental Veneers?
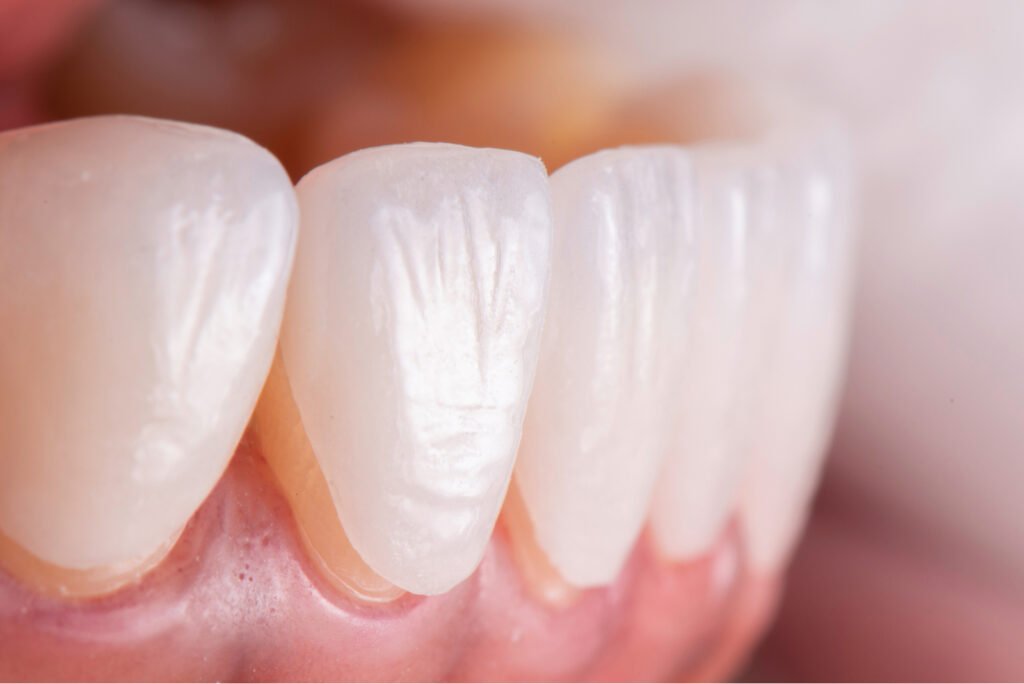
Dental veneers are thin, custom-made shells designed to cover the front surface of teeth, improving their shape, size, and color. They are often used to correct:
- Chipped or broken teeth
- Severe discoloration or staining
- Small or irregularly shaped teeth
- Gaps between teeth
- Uneven or worn-down teeth
Veneers are typically made from porcelain or composite resin and are permanently bonded to the natural tooth structure. While some patients may need a single veneer (for a chipped tooth), many choose 6–8 veneers for a symmetrical, uniform smile—especially for the top front teeth.
Types of Dental Veneers
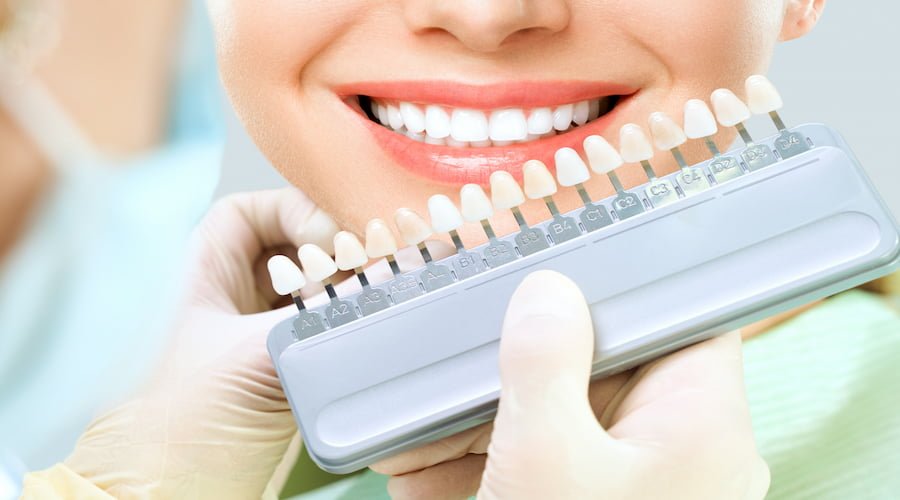

1. Porcelain Veneers
- Durable and natural-looking.
- Resistant to staining.
- Require more preparation, as a small portion of enamel must be removed.
- Usually made in a dental laboratory or with CAD/CAM technology in-office.
- Lifespan: 10–20 years with proper care.
2. Composite Resin Veneers
- Made directly on the tooth using a composite material.
- Require less enamel removal than porcelain.
- Usually completed in a single visit.
- More affordable but less durable (5–7 years lifespan).
- Easier to repair if damaged.
3. No-Prep Veneers (e.g., Lumineers, Vivaneers)
- Minimal or no enamel removal required.
- Less invasive and often painless.
- Can sometimes be placed without anesthesia.
- Typically last 5–7 years.
| Type | Material | Durability | Stain Resistance | Lifespan | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Porcelain Veneers | Porcelain/Ceramic | Very High | Excellent | 10–20 years | Most natural look & long-lasting |
| Composite Veneers | Composite Resin | Moderate | Fair | 5–7 years | Quick, affordable, repairable |
| No-Prep Veneers (Lumineers) | Ultra-thin Porcelain | Moderate | Good | 5–7 years | Minimal enamel removal, less invasive |
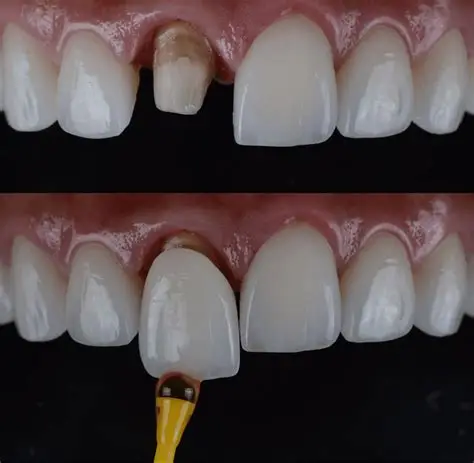
How Are Veneers Applied?
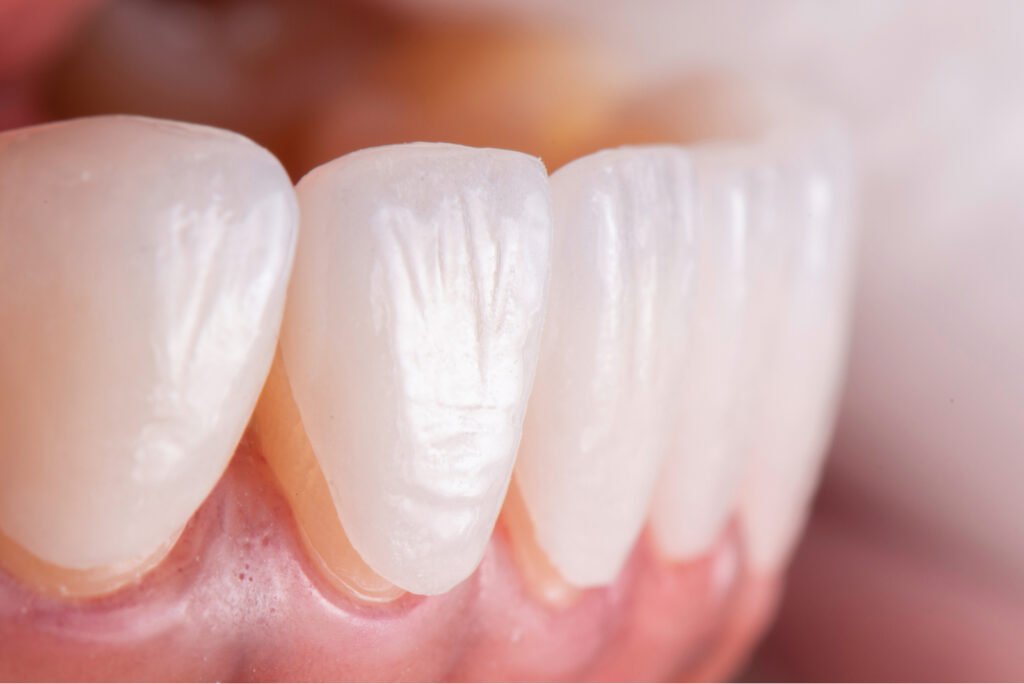
- Consultation & Planning
- Dentist evaluates your teeth with X-rays and impressions.
- A treatment plan is created based on your goals (shape, color, number of veneers).
- Tooth Preparation
- A thin layer of enamel (around 0.5 mm) is removed.
- For porcelain veneers, an impression is taken and sent to the lab.
- Temporary veneers may be placed while the permanent ones are made.
- Bonding
- Teeth are cleaned and slightly roughened for better adhesion.
- Veneers are positioned, adjusted, and bonded with dental cement.
- A curing light hardens the bond, and final adjustments are made.
The entire procedure typically requires two visits for porcelain veneers, but composite veneers are often completed in a single session.
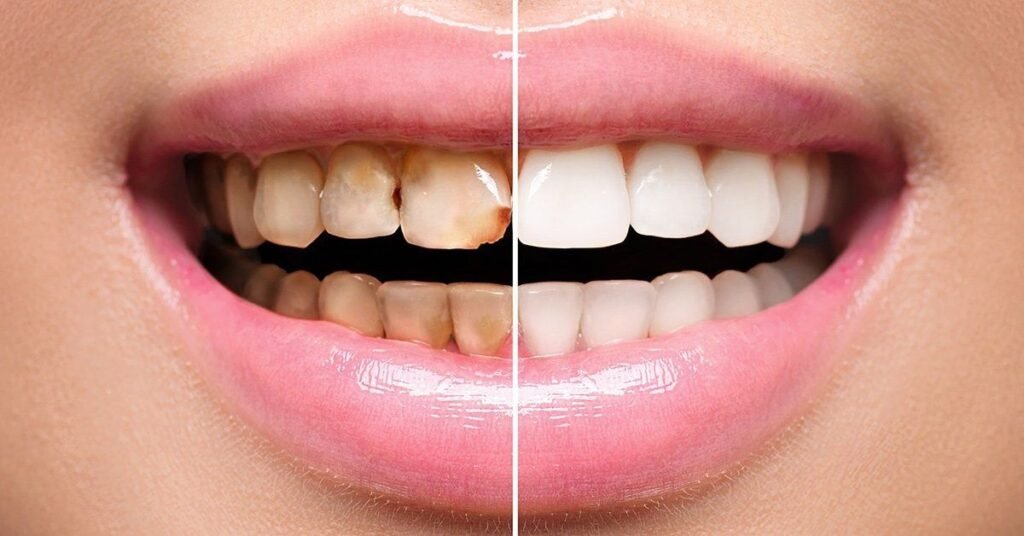
Benefits of Dental Veneers
- Improve the appearance of teeth and smile aesthetics.
- Long-lasting with proper care.
- Resistant to stains (especially porcelain).
- Provide a natural tooth-like appearance.
- Less invasive than crowns.
Pros and Cons of Dental Veneers
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Improves smile aesthetics | Irreversible (enamel removal required) |
| Stain-resistant (especially porcelain) | Can cause tooth sensitivity |
| Durable & natural appearance | Can chip/crack under pressure |
| Less invasive than crowns | Not suitable for patients with decay or gum disease |
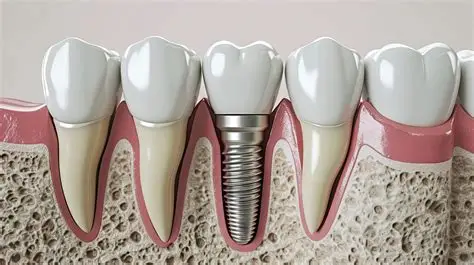
Veneers vs. Crowns vs. Implants
- Veneers – Cover only the front surface of the tooth; cosmetic-focused.
- Crowns – Encapsulate the entire tooth; used for protection and strength.
- Implants – Replace an entire missing tooth, including the root.
| Treatment | Covers/Function | When Used | Invasiveness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Veneers | Front surface of tooth | Cosmetic fixes: chips, stains, gaps | Minimally invasive (enamel shaving) |
| Crowns | Entire tooth surface | For damaged, weak, or root-treated teeth | Moderate–high (more tooth removal) |
| Implants | Replaces entire tooth + root | When tooth is missing completely | Surgical procedure |
Aftercare for Veneers
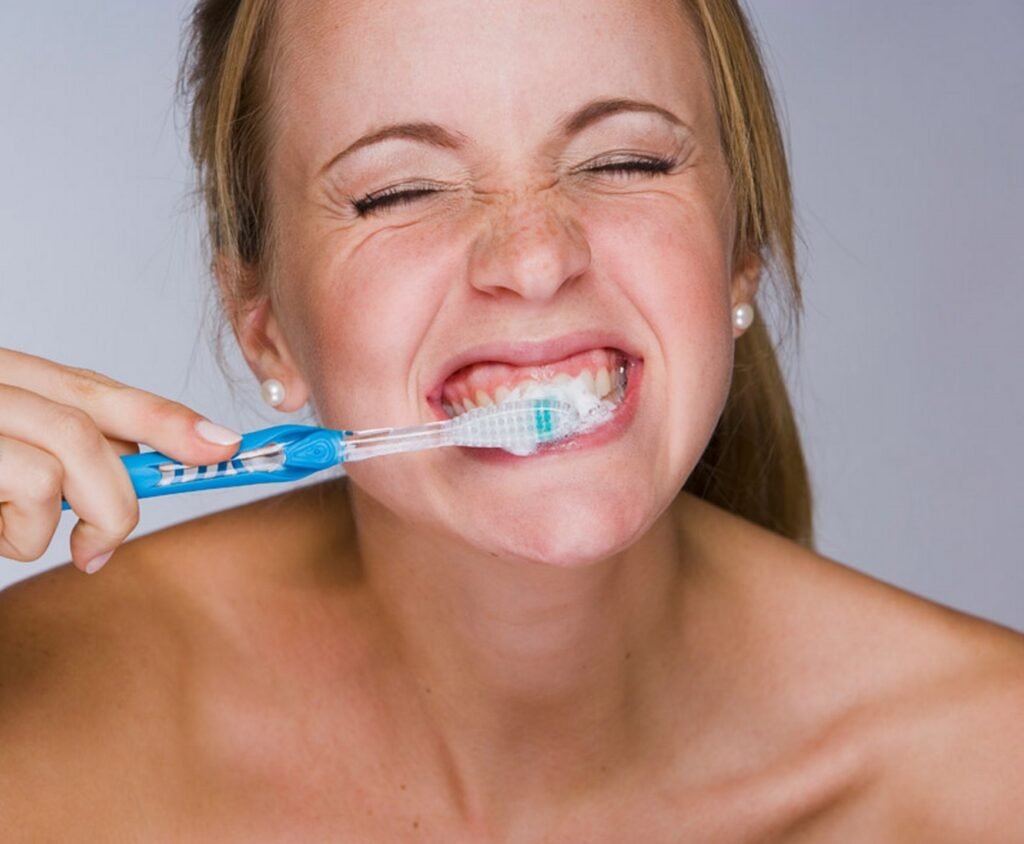

Dental veneers require the same care as natural teeth:
- Brush twice daily and floss regularly.
- Avoid chewing on hard objects (ice, pens, fingernails).
- Do not use teeth as tools (e.g., opening packages).
- Use a mouthguard if you grind/clench your teeth at night.
- Wear a sports mouthguard if playing contact sports.
With proper care, porcelain veneers last 10–20 years, while composite and no-prep veneers last 5–7 years.
Potential Risks & Considerations
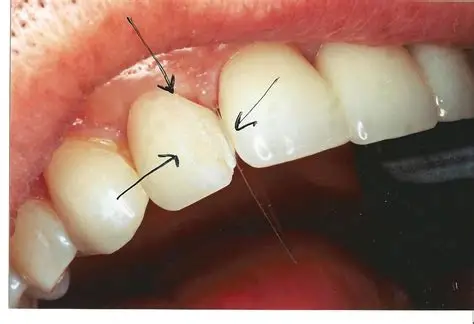
- Irreversible procedure (enamel removal).
- Teeth may become sensitive to hot/cold.
- Veneers can chip or crack under excess pressure.
- Not suitable for patients with untreated decay, gum disease, or severe misalignment.
Key Takeaway
Dental veneers are a minimally invasive cosmetic dental solution that can transform a smile by correcting shape, size, and color issues. With proper selection and care, they offer long-lasting results and significantly improve smile aesthetics.
Find Our Center
Use our interactive map to get directions to the closest abumaizar Center near you.
View Locations & HoursNeed Immediate Help?
Call us directly during business hours to speak with a patient coordinator.
Call: +962 79 5 931 831👨⚕️ Meet Your Expert Trusted care from a certified specialist.
Dr. Hasan AbuMaizar (DDS, Endodontist)
Board-certified endodontist in Amman, Jordan. Founder of AbuMaizar Dental Center. Master’s in Endodontics (Distinction) from the University of Manchester. Dedicated to clinical excellence and professional leadership.
Meet Dr. Hasan AbuMaizar